Asif Ahmed Neloy
I am a Lead Data Scientist/MLE with GM Training Arc, Vancouver, BC, where I build player-facing analytics for esports training using gameplay telemetry and video-based computer vision.
I am also an Adjunct Faculty member in the Faculty of Land and Food Systems at the University of British Columbia (UBC). I teach programming, algorithms, networking, computer vision, databases, machine learning, and analytics.
I received an MSc in Computer Science from the University of Manitoba under the supervision of Dr. Maxime Turgeon and Dr. Cuneyt Akcora. My thesis studied disentangled VAEs for unsupervised anomaly detection.
I work across end-to-end machine learning systems, from data ingestion and feature engineering to training, evaluation, deployment, and monitoring. My day-to-day tools include Python and SQL, deep learning with PyTorch, and production APIs using FastAPI with containerized workflows. I build reproducible pipelines with Airflow and PySpark, work with Snowflake and PostgreSQL for analytics and feature stores, and deliver decision-ready reporting in Power BI or Tableau. I also build and evaluate retrieval-based large language model assistants using embeddings and vector search, with careful logging, quality checks, and guardrails.
My research focuses on anomaly detection, representation learning, and probabilistic or Bayesian modeling, with an emphasis on unsupervised methods and reproducibility. I study auto-encoder families and variational formulations for high-dimensional data, and I publish practical comparisons that surface efficiency and trade-offs across model classes. My applied work spans natural language processing, computer vision, and governed analytics in population and health settings.
Earlier in my career, I held industry roles across supply planning and forecasting at Advanced Chemical Industries (ACI) Ltd, and portfolio and leasing analytics in real estate at Daris Properties Ltd. and Forum Inc.. I have also contributed to large language model evaluation work, focusing on factuality, safety, and user experience under detailed rubrics.
Recent News
- [August 2025] Led a week long MFRE bootcamp and workshop series on Python and R covering data access, visualization, and coding for economic analysis.
- [April 2025] Supervised graduate students in the UBC MFRE Summer Program.
- [November 2024] My paper titled "Disentangled Conditional Variational Autoencoder for Unsupervised Anomaly Detection" was accepted at the IEEE Big Data Conference (IEEE BigData 2024), Washington, D.C., December 15-18, 2024. IEEE Xplore
- [July 2024] My paper titled "A Comprehensive Study of Auto-Encoders for Anomaly Detection: Efficiency and Trade-offs" was published in Machine Learning with Applications. ScienceDirect
- [June 2024] Received Research Dissemination Present and Research Dissemination Publish Grant from Douglas College
- [December 2023] Joined Douglas College, New Westminster Campus as a Full-time Regular Faculty Member.
- [August 2023] Started my new journey as a Faculty Member at the Vancouver Island University.
- [May 2023] Promoted to Machine Learning Engineer, Daris Properties Ltd.
- [February 2023] Latest published conference paper - Feature Extraction and Prediction of Combined Text and Survey Data using Two-Staged Modeling
- [January 2023] My MSc dissertation, Dimension Reduction and Anomaly Detection using Unsupervised Machine is now online
- [November 2022] Guest Lecture, Introduction to Python and Numpy, STAT 447: Statistical Machine Learning for Data Science, Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Saskatchewan
- [September 2022] Received Graduate Travel Award from University of Manitoba, NSERC CREATE VADA Program
Projects
Research
My work centers on anomaly detection, representation learning, and probabilistic or Bayesian modeling, with an emphasis on unsupervised methods and reproducibility. I study auto-encoder families and variational formulations for high-dimensional data, build governed analytics for population health settings, and publish practical comparisons that surface efficiency and trade-offs across model classes.
Unsupervised Anomaly Detection
Disentanglement in latent spaces, total-correlation objectives, and conditional VAEs for detecting rare structure in image and tabular data.
Representation Learning
Comparative studies of auto-encoder architectures that quantify reconstruction quality, sampling behavior, latent visualization, and classification accuracy.
Applied Health Analytics
Population-scale modeling with governance, documentation, and repeatable pipelines as part of the NSERC CREATE VADA program.
NLP & Information Retrieval
RAG systems, document processing, text classification, and evaluation frameworks for language model applications.
Teaching
- FRE 501: Topics in Food Market Analysis (Co-instructor)
- CSIS 3300: Database II
- CSIS 3360: Fundamentals of Data Analytics
- CSIS 4260: Special Topics in Data Analytics
- CSIS 1175: Introduction to Programming I
- CSIS 2200: Systems Analysis & Design
- CSIS 3860: Data Visualization
- CSIS 2300: Database I
- CSIS 3300: Database II
- CSIS 3360: Fundamentals of Data Analytics
- CSIS 2200: Systems Analysis & Design
- CSIS 2300: Database I
- CSIS 3290: Fundamentals of Machine Learning in Data Science
- CSCI 251: Systems and Networks
- CSCI 159: Computer Science I
- CSCI 112: Applications Programming
- DATA 2010: Tools and Techniques for Data Science
- COMP 3490: Computer Graphics 1
Guest Lectures and Seminar Presentations
Invited Sessions
Topic: Auto-encoders for Anomaly Detection: Efficiency and Trade-Offs.
Lectures
Publications
See my Google Scholar profile for the most recent publications.
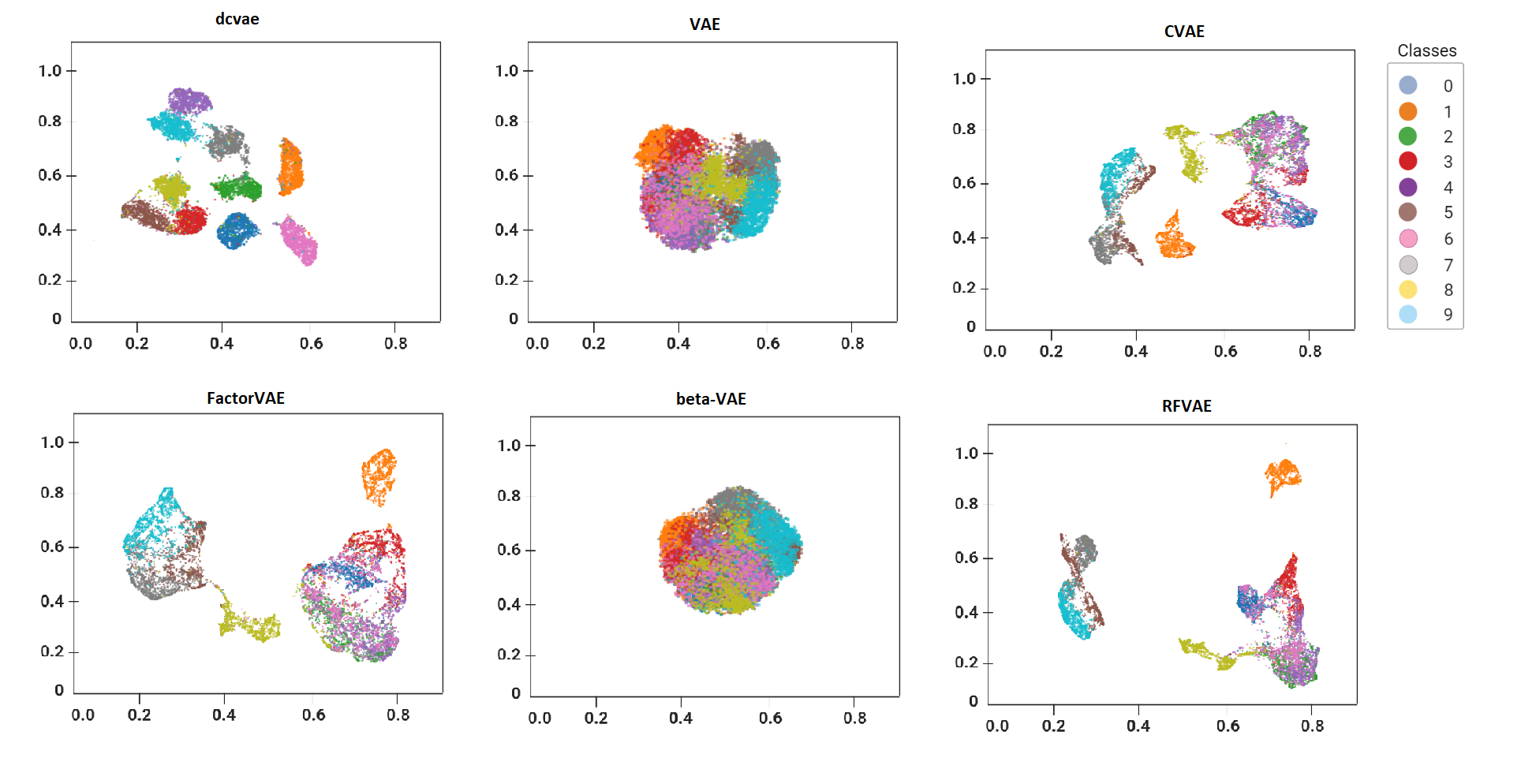
A novel generative architecture combining beta-VAE, CVAE, and total correlation to enhance feature disentanglement and improve anomaly detection in high-dimensional datasets.
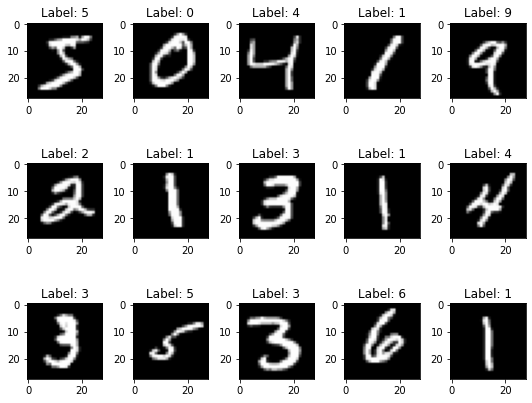
Systematic review of 11 Auto-Encoder architectures, analyzing reconstruction ability, sample generation, latent space visualization, and anomaly classification accuracy.
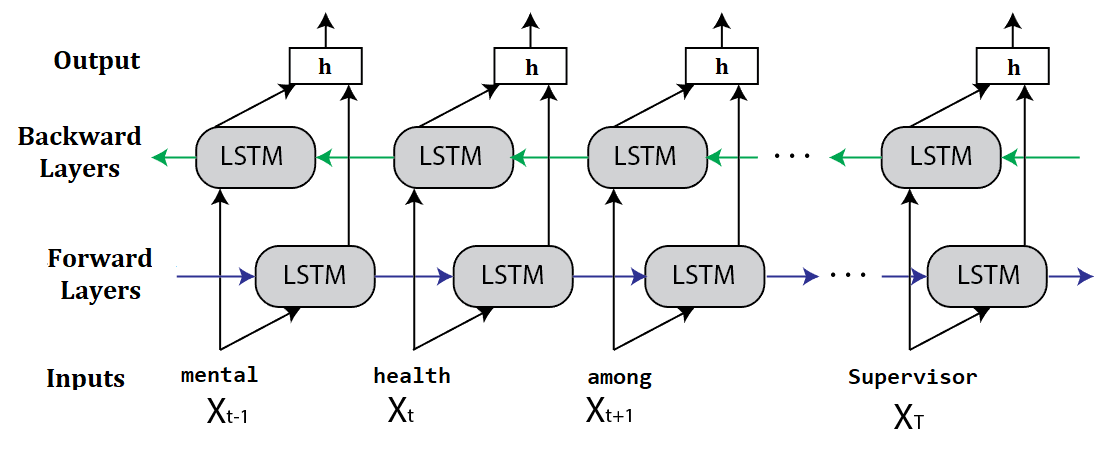
Two-stage modeling approach combining stacked ensemble classifiers with CNN and bidirectional RNN for NLP problems in real-world datasets.
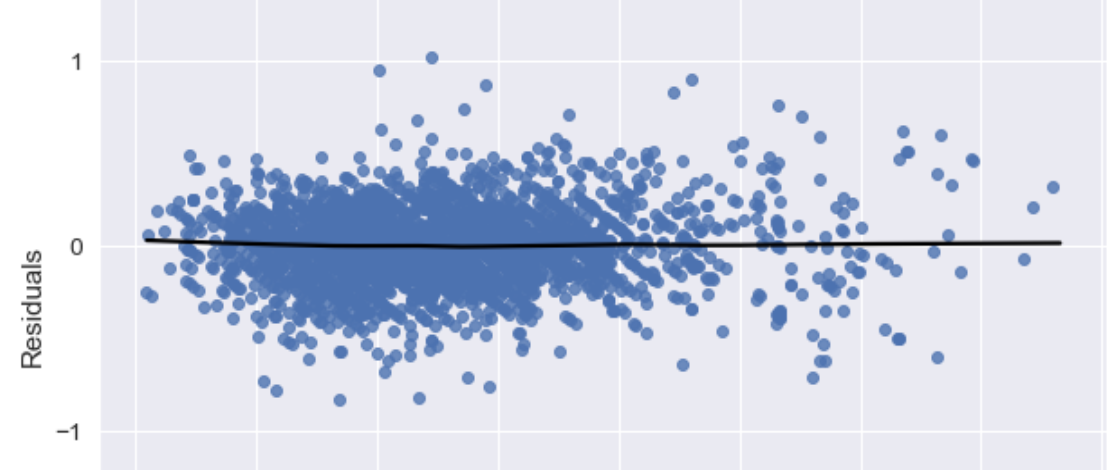
Apartment rental price prediction using categorical feature factoring and ensemble learning, comparing tree-based and boosting methods.
Python Packages
Open-source Python library to select the appropriate data scaler for your Machine Learning model.
Python open-source library to convert color or B&W image to pencil sketch.
Open-source Python package to clean and prepare your dataset before applying a machine learning model.
